Experiential Learning (EL) Activities
Experiential learning creates a deeper understanding of course content, promotes critical thinking and problem-solving, and allows students to actively participate, reflect, and apply new knowledge and skills. The goal of Civil Engineering Experiential Learning (EL) activities encompass lifelong learning, design process, and embodying interdisciplinary interventions for solving open ended problems. Experiential learning activities provide opportunities for students to explore the synergies between different disciplines. By engaging in hands-on projects and practical applications, students not only enhance their theoretical understanding but also develop crucial skills and insights that are vital for success in the modern world.
EL Coordinator: Dr. Shweta Goyal
|
Semester 1: Design and Analysis of truss bridge |
|||
|
Designing is one of the critical components of Civil Engineering. Only by actively participating in the design process we can completely comprehend the challenges and rewards of engineering. This activity will introduce first year students to core civil engineering aspects and real-world situations that involves bridges, roof trusses and various building sections. In this learning activity, students will construct a truss bridge structure from the provided materials. This activity will provide Students with valuable preparation for learning how to design a structure. Students will be able to observe how the structure works and understand about various structural members and the joint system. The group will comprise maximum of 5 members. Faculty Facilitator Dr. Arpit Goyal |
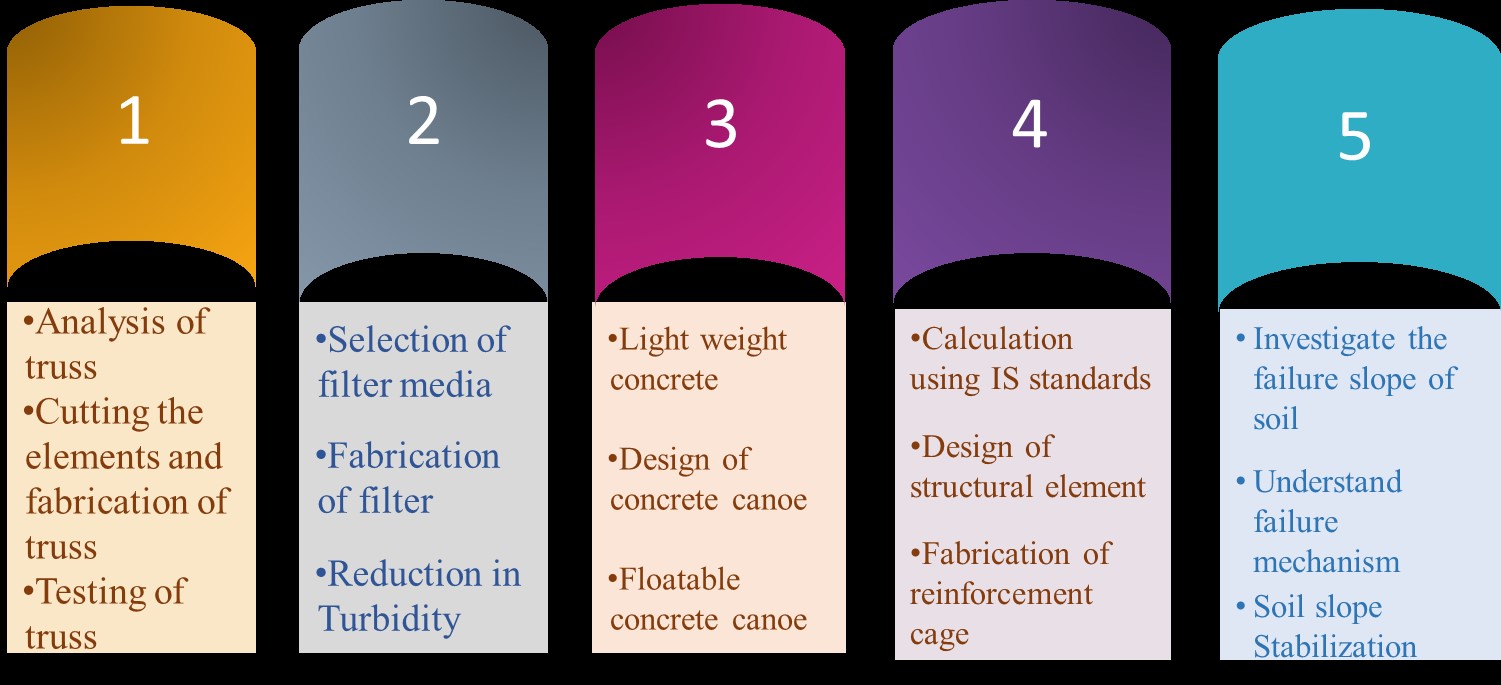
The basic outline of the activity is:
After going through this activity the students would be able to:
|
||
|
Semester 2: Deployment of a filtration unit in a municipal area |
|||
|
This ELC activity was planned for BE-First Year Civil Engineering Students. This activity was a group activity. At this stage, students are aware about water quality but talking in terms of water quality parameters is not in their look around. Therefore, the purpose of this activity was to make students illustrate water quality in terms of water quality parameters. Water quality parameter taken for this activity was Total Suspended Solids (TSS), as it is simpler to understand and comprehend. With an introductory lecture, on understanding TSS, why it is undesirable and how it can be controlled. Faculty Facilitator Dr. Richa Babbar |
The basic outline of the activity is:
Students were expected to undertake the activity in the following steps:
At the end of ELC activity, students have knowledge of
|
||
|
Semester 3: Concrete canoe: development of floatable concrete |
|||
|
The goal of this activity is to expose the students to the use of light-weight materials to design a light weight economic concrete mix to carry the self-weight and maximum live load in floating condition. In this activity students learn to apply the guidelines given in Indian standard for product design and fabrication. In this process, they learn about material selection, geometrical design, mould fabrication, casting of concrete, testing and filed implementation of products.
Faculty Facilitators
Dr. Gurbir Kaur Dr. Vivek Gupta |
The basic outline of the activity is:
Concrete Mix Design:
Canoe Design and Mold Construction:
Concrete Casting:
Finishing and Reinforcement:
Testing and Evaluation:
|
||
|
Semester 4: REINFORCEMENT DETAILING OF STRUCTURE ELEMENTS |
|||
|
In this activity, students are given a building, firstly they need to determine the dimensions of all structural elements, such as beams, columns and slab. Further, they need to calculate the loading acting on these elements and also they have to use the Indian standard codes to determine the self-weight of structural elements using unit weight material. Based on the load calculation, students have to design the structural elements using IS 456:2000 and develop the reinforcement detailing of structural elements. At the end, using reinforcement drawings, students have to fabricate the reinforcement cage using steel wires. Faculty Facilitator Dr. Himanshu Chawla |
The basic outline of the activity is:
After going through this activity the students will be able to :
|
||
|
Semester 5: Slope stability analysis of soil |
|||
|
The primary objective of this activity is to introduce students to concepts of slope failure and stabilization through innovative ways. The activity instills capacity in students to critically think about problems which have real-life importance.
Faculty Facilitator
Dr. Aditya Parihar Mr. Rajesh Pathak |
The basic outline of the activity is:
Introduction to Slope Stability:
Soil Classification:
Slope Geometry:
Hands-on Analysis:
Data Interpretation:
Discussion and Conclusion:
|
||